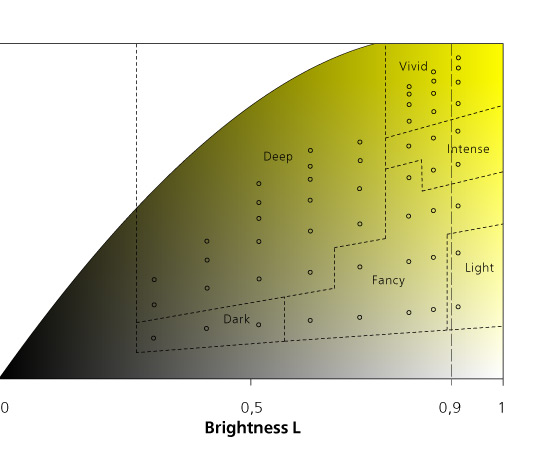
 If a hue is fixed, for example, yellow, all colors of this hue described in terms of Saturation and Brightness of through Chroma and Brightness. Two diagrams here have the same horizontal coordinate: brightness but different vertical one on the left - saturation , on the right - chroma. The described technology supports both of these types of coordinates. There is an open question: which representation is the better to describe human abilities to differentiate color and describe this difference. On these pictures the positions of Munsell yellow chips used for color grading on the both diagrams are indicated as blank circles. First we recognize the position of Munsell chips on this diagram (different color system cross reference tables were used). After this we have used color grades for each Munsell chip according to the GIA paper published in Gems&Gemology in 1994.
|